Newton Raphson method in c
In numerical analysis, Newton's method (also known as the Newton–Raphson method), named after Isaac Newton and Joseph Raphson, is a method for finding successively better approximations to the roots (or zeroes) of a real-valued function.
Features of Newton Raphson Method:
- Type – open bracket
- No. of initial guesses – 1
- Convergence – quadratic
- Rate of convergence – faster
- Accuracy – good
- Programming effort – easy
- Approach – Taylor's series
Program of Newton Raphson in C
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<math.h>
#define e 0.001
#define F(x) (2*x)-3
float frac(float a)
{
float f1;
f1=a*a-3*a+2;
return f1;
}
void main()
{
float x1,x2,f1=0,f2,er,d;
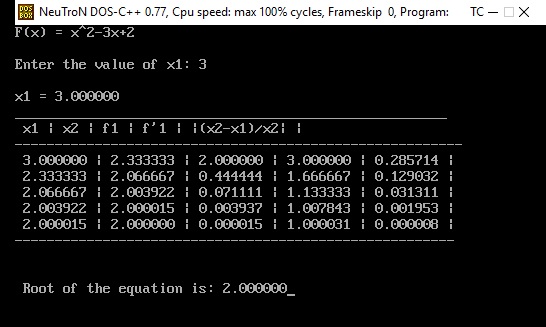
printf("F(x) = x^2-3x+2\n\n");
printf("Enter the value of x1: ");
scanf("%f",&x1);
printf("\nx1 = %f",x1);
printf("\n______________________________________________________\n");
printf(" x1 | x2 | f1 | f'1 | |(x2-x1)/x2| | \n");
printf("--------------------------------------------------------\n");
do
{
f1=frac(x1);
d=F(x1);
x2=x1-(f1/d);
er=fabs((x2-x1)/x2);
printf(" %f | %f | %f | %f | %f | \n",x1,x2,f1,d,er);
x1=x2;
}
while(er>e);
printf("-------------------------------------------------------\n\n");
printf("\n Root of the equation is: %f",x2);
getch();
}
Output